BeamNG.tech v0.38 puts vehicle prototyping front and center with a significantly expanded Template Car workflow. The Template Car itself has been improved to serve as a more practical starting point for custom builds, with additional body styles (Coupe, Wagon, Pickup), more configuration options across suspensions and hubs, better material/color support, working powertrain sound/torque reactions, and general fixes that make it behave more predictably during development. On top of that, v0.38 introduces the new Template Car Generator, a simple tool for generating parameterized template vehicles by selecting body dimensions, body styles, and suspension layouts and iteratively dialing in mass and center of gravity. It’s designed to give you a solid, editable baseline you can quickly adapt for sensors, custom powertrains, AI/controller testing, and experimental setups.
BeamNGpy updates land in the same release, focusing on more reliable automation and easier deployment. Deterministic mode gains a speed_factor option for faster-than-realtime stepping, connection/reconnection handling has been improved (including better behavior when BeamNG.tech is closed), and new vehicle queries expose mass properties and node/reference-node information. BeamNGpy can also launch BeamNG.tech with more control (headless mode, null-graphics/no-GPU mode, selectable rendering APIs), and can report the effective launch arguments for reproducibility. Complementing this, headless deployments can now run without a GPU via -gfx null and the release includes a no-GPU Docker Compose template, while editor tooling improves sensor iteration with simultaneous multi-sensor live previews.
In addition, v0.38 extends the BeamNG-ROS2 bridge with drone controller support, introducing a ROS2-based keyboard teleoperation system for controlling drone vehicles in BeamNG.tech. The controller translates messages on the /drone_control topic into Lua commands for the simulator’s droneInput controller, enabling real-time flight control (takeoff/land, movement, and orientation) through a modular four-node architecture consisting of the bridge, scenario loader, controller, and teleop nodes.
Here’s a quick look at what’s new:
BeamNGpy
- Added the
speed_factorargument toBeamNGpy.settings.set_deterministic.
Can be used for faster-than-realtime simulation, as explained in the documentation and in theexamples/faster_than_realtime.pyBeamNGpy example. - Added an error log on BeamNG.tech side if BeamNGpy protocol versions mismatch.
- Fixed crashes which happened when using the JBeam Editor Visual Studio Code extension and BeamNGpy at the same time.
- Fixed the
-tcom-captureargument not automatically loading thetechCoreextension. - Added ESC control functions
- Fixed Vehicle.deflatetire(wheelid: int) deflating all tires instead of the chosen one
- Added annotation support for procedural objects.
You can check the updated example for the usage. - Added
TemplateCarGeneratorclass for programmatic use of the new Template Car Generator - Made examples overview page available in BeamNGpy documenation
- Added new functions
get_mass_properties,get_ref_nodesandget_node_infoto theVehicleclass
These functions allow the user to get a vehicle’s current mass properties, including total mass, center of gravity and inertias, get information about the vehicle’s reference nodes as well as the mass and current position of every desired node. - Improve connection and reconnection to BeamNG.tech
- We now detect if BeamNG.tech was closed and stop doing further connection attempts in this case, for a more responsive user experience
- Fixed some bugs in the connection/reconnection code
- Lowered connection attempt time intervals for faster response time
- Added more launch arguments to the BeamNGpy object.
BeamNGpy(..., headless=True)- Will start BeamNG.tech in headless mode (server mode, no window is used, GPU is required).BeamNGpy(..., nogfx=True)- Will start BeamNG.tech with the null graphics mode (does not require a GPU, camera-based sensors are unavailable).BeamNGpy(..., gfx=GFX)- Will start with the specified rendering API. Possible values aredx11(only on Windows),vk, andnull.
- Added the
BeamNGpy.get_launch_arguments()function to return a command-line string which would be or was used to launch BeamNG.tech.
Lua API
- Reduced overhead by calling
tech_techCore.refreshScenarioListonly when needed.
Headless Mode
- Implemented support for running without a GPU.
Use the-gfx nullargument, which can be combined with headless mode. - Added a no-gpu Docker template.
It can be found in the BeamNG.tech release archive in the/tech/docker/docker-compose-nogpu.yml. Documentation available on the Headless Mode page.
Vehicles
-
Template Car
- Adjusted jbeam to simplify scaling needed for DAE meshes
- Added different body styles (Coupe, Wagon, Pickup)
- Added more hub options for all suspension types
- Added colorable material to main shape and added predefined colors
- Added working engine sounds and engine torque reactions
- Fixed some issues with certain suspensions
- Fixed body deforming too easily




-
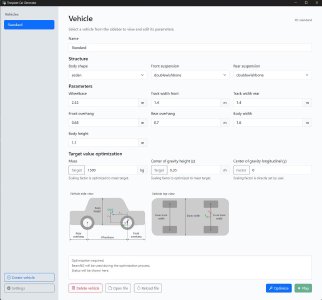
Template Car Generator
- Added ability for parametrizeable template cars to be generated.
- Different body dimensions, body styles, and suspensions can be selected. Mass, and center of gravity position can be adjusted via an iterative loop due to interdependence of these properties.
- Simple user interface used to generate the cars
- These are a good basis for more advanced user to build on top of and modify to suit their requirements (such as adding sensors, testing custom powertrains, testing custom AI, etc.)
- For more detailed information, check out the documentation for usage instructions, and BeamNGpy for more details on using this tool programmatically via Python scripts.




World Editor
- Added live previews for Advanced IMU and Ultrasonic sensors in the Sensor Configuration Editor
- Multiple live previews can be viewed simultaneously in the Sensor Configuration Editor
ROS2
Drone controller is added to BeamNG-ROS2 bridge: ROS2-based keyboard teleop system that controls a BeamNG.tech drone vehicle by translating ROS2 /drone_control topic messages into Lua commands for the simulator’s droneInput controller, enabling real-time flight control (takeoff/land, movement, orientation) through a 4-node architecture (bridge, scenario loader, controller, teleop)
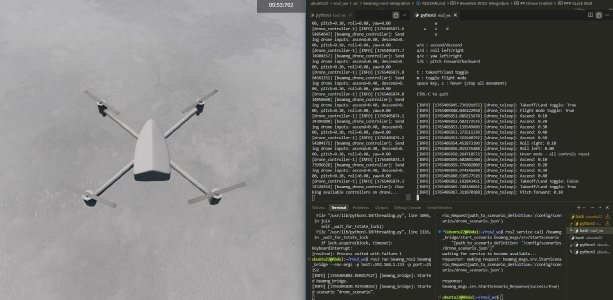
Limitations
While the ROS2 drone support introduces real-time control and a streamlined teleoperation pipeline, there are a few current limitations in drone mod itself and it’s control:
- The drone is highly sensitive to disturbances; minor impacts or abrupt descents can cause unrecoverable instability.
- Lack of a fixed camera option can make the flight experience disorienting.
- Default keyboard controls do not yet support digital input for roll and pitch, limiting usability without analog devices.
- The drone’s total available thrust is disproportionately high for its size and may require tuning for more realistic behavior.
- Visual artifacts such as camera shake and zoom inconsistency may occur during unstable flight.
Future updates will aim to address these areas.
